Block Elements
You already know about HTML inline elements. All HTML tags have specific display behavior: they are either block-level elements or inline elements.
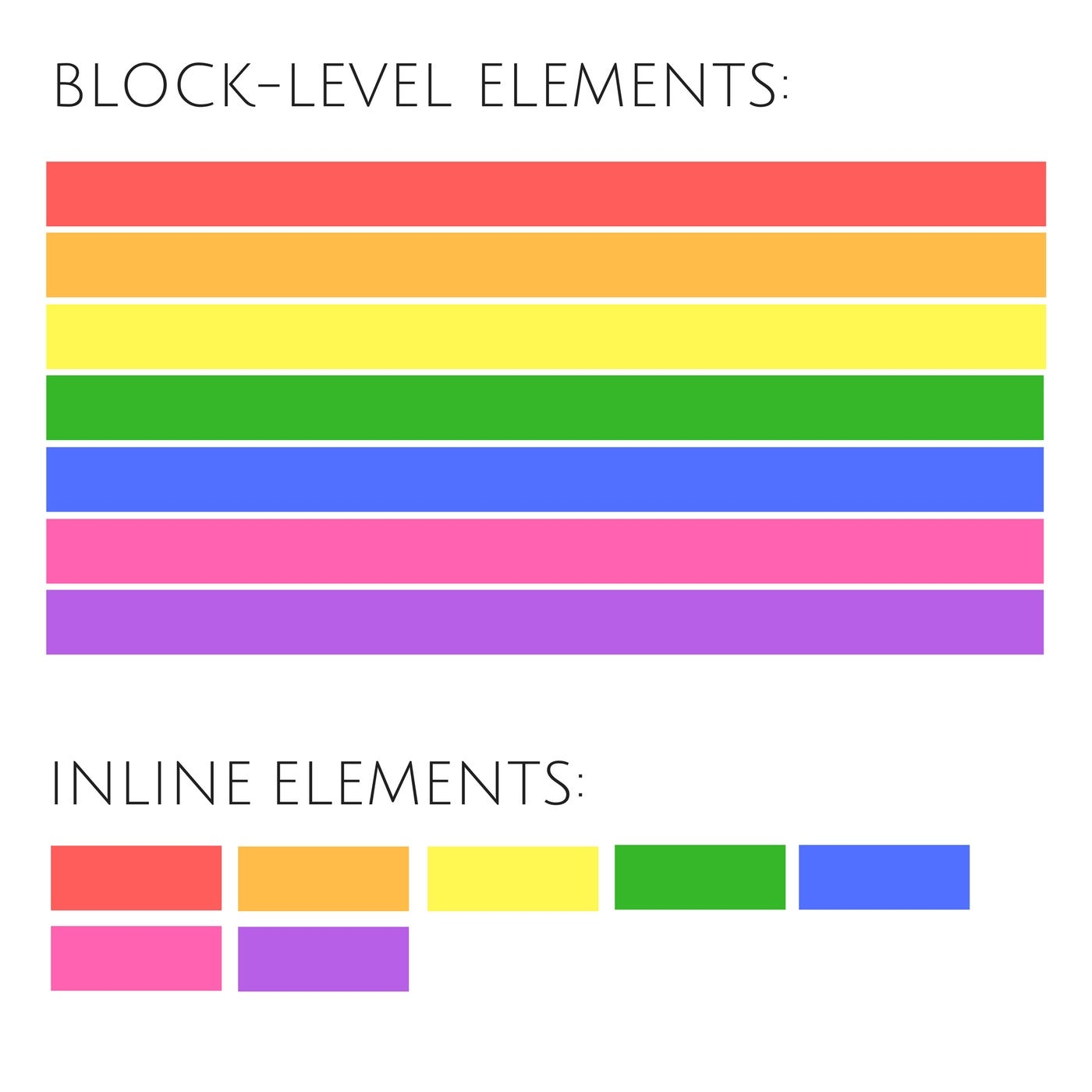
What are Block-level Elements?
Block-level elements are those that start on a new line and take up the entire width of their container by default. They essentially claim all the horizontal space for themselves, pushing any content that comes after them to a new line.
Characteristics of Block-level Elements:
- Always start on a new line.
- Take up the full width available.
- Width and height can be controlled via CSS.
- Can contain other block-level as well as inline elements.
Common Block-level Elements:
<h1>,<h2>,<h3>,<h4>,<h5>,<h6>- Headings<p><hr><address><article><aside><blockquote><canvas><dd><div><dl><dt><fieldset><figcaption><figure><footer><form><header><li><main><nav><noscript><ol><ul><pre><section><table><video>
Inline Elements
Inline Elements don't start on a new line. They only take up the width required to cover the content.
HTML elements are generally divided into two categories: Block-level and Inline elements.
Styling Inline Elements
You can use CSS to style inline elements. However, some properties like width and height may not apply.
List of Inline Elements:
<a><abbr><acronym><button><br><big><bdo><b><cite><code><dfn><i><em><img><input><kbd><label><map><object><output><tt><time><samp><script><select><small><span><strong><sub><sup><textarea>